In the narrow sense, 3D printing technology mainly refers to additive molding technology. From the molding process, 3D printing technology breaks through the traditional molding method by combining the rapid automatic molding system with the computer data model without any additional traditional mold manufacturing and machining. The ability to produce prototypes of various shapes and complexities has greatly shortened the design and production cycle of the products and drastically reduced production costs.
Common 3D printing technology
SLA (Stereo LithographyApparatus, selective curing of photosensitive resin)
SLS (Selective LaserSintering, selective laser sintering of powder materials)
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling, fused deposition)
3DP (3Three DimensionPrinting, 3D Jet Printing)
PUG (Poly-Urethan-Guss, vacuum injection type)


1.SLA (light curing technology)
Stereolithography Apparatus (SLA), also known as stereolithography. The process was first proposed by Charles W. Hull in 1984 and obtained the US national patent. It was one of the earliest developed 3D printing technologies. Charles W. Hull founded 3D Systems two years after the patent was acquired and in 1988 released the world's first commercial 3D printer SLA-250. The SLA process has also become a 3D printing technology with the deepest research, the most mature technology and the most widely used technology in the world.
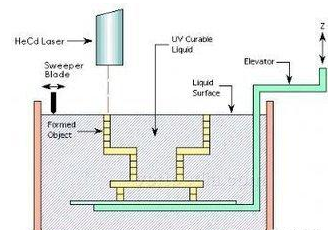
Figure: SLA (Photocuring Technology) Schematic
Principle: The liquid tank is filled with liquid photosensitive resin first. The ultraviolet laser beam emitted by the cadmium-cadmium laser or the argon ion laser is carried out by the computer under the control of the layered cross-section data of the workpiece on the surface of the liquid photosensitive resin. Point scanning, which causes the thin layer of resin in the scanning area to polymerize and solidify from a thin layer forming the workpiece.
After the curing of a layer of resin, the workbench will be moved down by a layer thickness to cover a layer of new liquid resin on the surface of the previously cured resin. The squeegee will smooth the surface of the resin with higher viscosity and then The next layer of laser scanning is cured.
Advantages and disadvantages of SLA (light curing technology)
advantage:
1. The molding process is highly automated.
2. High dimensional accuracy. The dimensional accuracy of the SLA prototype can reach ±0.1mm.
3. Excellent surface quality.
4. The system has a higher resolution and can make models or parts with more complicated structures.
Disadvantages:
1. Parts are more easily bent and deformed and require support.
2. Equipment operation and maintenance costs are high.
3. There are fewer types of materials that can be used.
4. Liquid resin has odor and toxicity and needs to be protected from light.
5. The liquid resin cured parts are brittle and easy to break.
2.SLS (Powder Sintering Technology)
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), first developed by CRDechard of the University of Texas at Austin in 1989 in its master's thesis, followed by CRDechard founded DTM and released in 1992 Sinterstation, an industrial grade commercial 3D printer based on SLS technology.
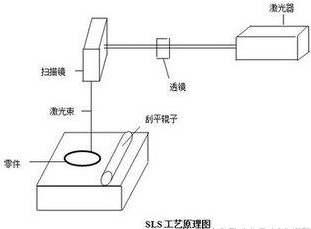
Figure: Schematic diagram of powder sintering technology
Principle: Firstly, a layer of powder is laid on the upper surface of the formed workpiece by a pressure roller, and the numerical control system controls the laser beam to scan the powder layer according to the cross-sectional profile of the layer to raise the temperature of the powder to the melting point, thereby performing sintering. Bonding is achieved in the molded part below. When the layer is sintered, the table will be lowered by a layer thickness. At this time, the pressure roller will evenly spread a layer of powder on it and start the sintering of the new layer section. The workpiece is completely formed by repeated operations.
Advantages and disadvantages of SLS (Powder Sintering Technology)
advantage:
Metal parts can be made directly (exclusive).
A wide range of materials are available.
Complex components or molds can be manufactured.
There is no need to add base support.
Material utilization
Disadvantages:
The sample surface is rough and appears granular.
Harmful gases are generated during processing
3.FDM (Fused Deposition Technology)
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is a 3D printing technology developed after the LOM process and the SLA process. The technology was invented by Scott Crump in 1988, and then Scott Crump founded Stratasys. In 1992, Stratasys launched the world's first 3D printer based on FDM technology - "3D Modeler", which also marks the FDM technology into the commercial stage.
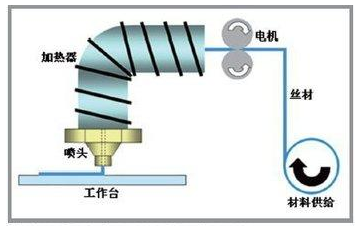
Figure: FDM (Fused Deposition Technology) Schematic
Principle: The filament-shaped hot-melt material is heated and melted, and the material is extruded through an extruder with a fine nozzle. The nozzle can be moved in the direction of the X axis, and the table moves along the Y axis and the Z axis (of course, the mechanical design of different devices may be different), the molten wire is extruded and then the previous layer The materials are bonded together. After the deposition of a layer of material, the table will be lowered by a predetermined increment and then the above steps will be repeated until the workpiece is fully formed.
Advantages and disadvantages of FDM (melt deposition)
advantage:
The whole system is simple in construction principle and operation, low in maintenance cost, and safe in system operation. Non-toxic raw materials can be used and the equipment system can be installed and used in an office environment.
The process is clean, simple, easy to operate and produces no waste.
The unique water-soluble support technology makes it easy to remove the support structure, and can quickly build bottle or hollow parts as well as one-time assembly structure.
The raw materials are supplied in roll form, easy to handle and quick to change.
A variety of materials are available, such as engineering plastics ABS, PC, PPSF and medical ABS in various colors.
Disadvantages:
The molding accuracy is lower than the SLA process with an accuracy of 0.178mm.
The profiled surface finish is not as good as the SLA process.
The molding speed is relatively slow.
4.3DP (3D Jet Printing Technology)
Polymer jet technology is a patented technology introduced by Israel Objet in early 2000. PolyJet technology is also one of the most advanced 3D printing technologies. Its molding principle is similar to that of 3DP, but it is not a binder but a polymer molding material. As shown in the figure, the structure of the PolyJet polymer injection system:
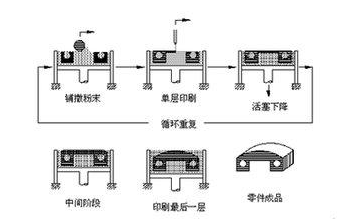
Figure: 3DP (3D Jet Printing Technology) Schematic
Principle: The 3D printed material is sprayed onto the build tray in an ultra-thin layer, cured with UV light, and can simultaneously eject two different mechanical properties. After a layer of jet printing and curing, the built-in workbench reduces the thickness of the forming layer with extreme precision. The nozzle continues to spray the photopolymer to print and cure the next layer. This is done one layer after another until the entire workpiece is printed.
Advantages and Disadvantages of 3DP (3D Jet Printing Technology)
advantage:
Two or more material combinations are produced at the same time.
The leather texture is clear, especially suitable for the trial production of interior parts (steering wheel, armrests, gears, etc.).
Sealing strips and sealing rings are trial-produced.
Make complex sub-assembly parts in one go.
More detailed performance details.
Small model making inside and outside.
Disadvantages:
Material strength is limited
5.PUG (vacuum injection technology)
The vacuum injection molding technology is based on the technology of the silicone mold to reproduce the sample, and the silicone mold manufacturing process is a relatively popular rapid mold manufacturing method. Due to the good flexibility and elasticity of the silicone mold, it is possible to produce parts with complicated structure, fine pattern, no draft angle, even inverted mold inclination and deep groove type, and the production cycle is short and the quality of the workpiece is high.
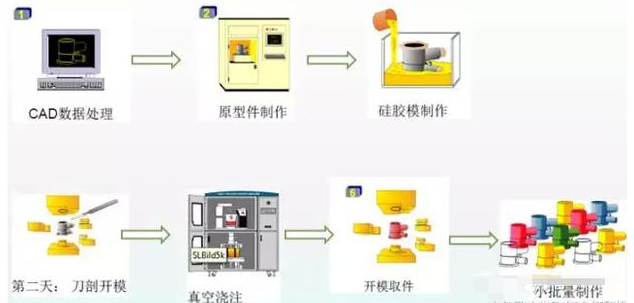
PUG process flow chart
advantage:
Small batch production.
The process is relatively simple and easy to operate.
Only a simple silicone mold is required, and the production time is short.
A variety of materials are available.
Disadvantages:
Class batch materials are limited in performance.
It is prone to surface defects such as foaming and lack of material.
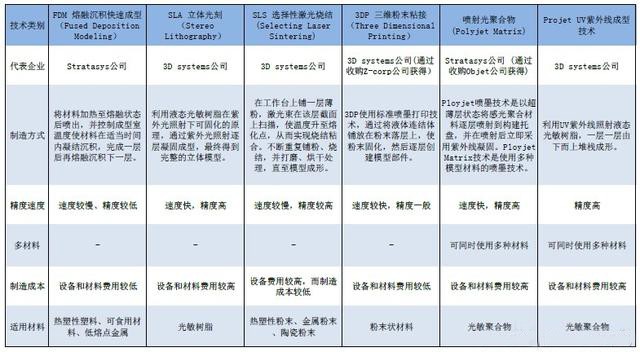
6. Five technical comparisons
Decor Globe,Decorative Desktop Globe,Desktop Globe With Stand,Vintage Decorative Globe
Ningbo Holly Arts & Crafts Co.,Ltd. , https://www.world-globe.com
